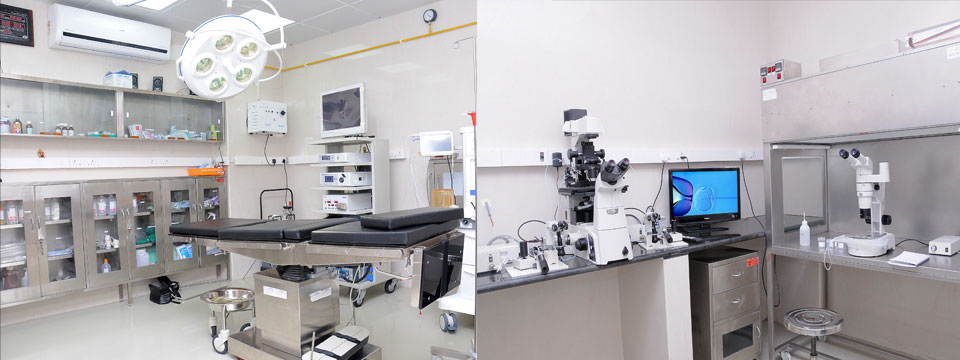
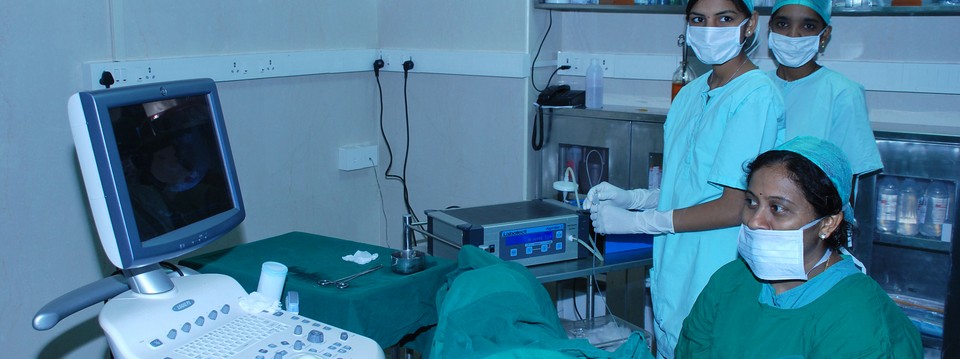
Uterine factors
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus, grows outside the uterus and attaches to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other organs in the abdominal cavity. Blood flow from the endometrial tissue is restricted and can cause inflammation and form scar tissue which can block the fallopian tubes or interfere with ovulation.
Fibroids
Fibroids are also known as leiomyomas. They can develop from the smooth muscle cells of the uterus and can interfere with pregnancy in many ways. The ones that grow on the inside wall of the uterus can cause changes in the endometrial tissue, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to attach to the uterine wall. Fibroids that develop outside the uterus can interfere with pregnancy by compressing or blocking the fallopian tubes, thereby preventing the sperm from reaching the egg.
Recurrent Miscarriage
Recurrent Miscarriage is defined as 3 or more consecutive, spontaneous pregnancy losses. Approximately 20 percent of pregnancies end in miscarriage, which is defined as the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation. Most miscarriages occur within the first 12 weeks of gestation. When miscarriage occurs this frequently, there may be underlying causes such as genetic factors, an abnormally shaped uterus, uterine fibroids, or scar tissue in the uterus which may hinder implantation or growth of the fetus. Hormonal imbalances or illnesses such as diabetes or immune system abnormalities may increase the chance of miscarriage.