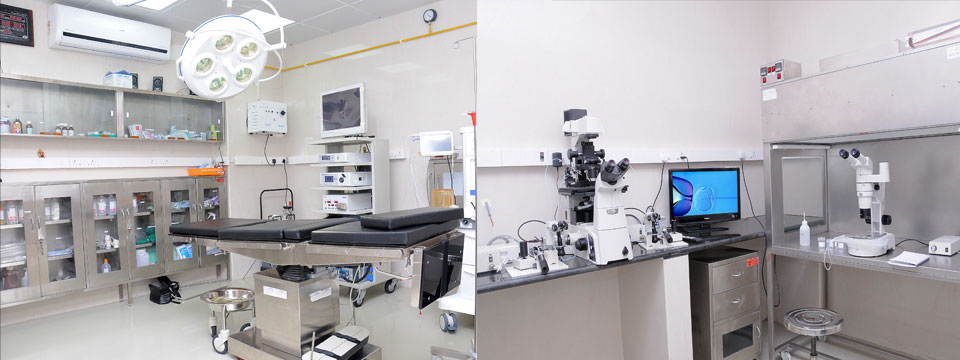
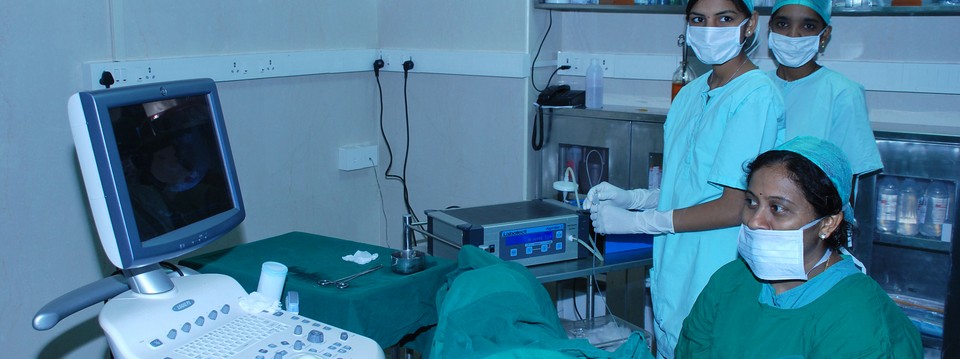
Patient Guide
How your infertility is treated depends on the cause, your age, how long you've been infertile and personal preferences. Although some women need just one or two therapies to restore fertility, it's possible that several different types of treatment may be needed before you're able to conceive.
Treatments can either attempt to restore fertility — by means of medication or surgery — or assist in reproduction with sophisticated techniques.
Treatment of infertility depends on the cause, how long you've been infertile, your age and your partner’s age, and many personal preferences. Some causes of infertility can't be corrected. However, a woman can still become pregnant with assisted reproductive technology or other procedures to restore fertility.
Treatment for men
A common misperception is that infertility is largely a female problem. In truth, approximately 50% of cases involve male factor infertility as well.
Identifying any underlying conditions that may affect a man's fertility prior to initiating any treatments can help spare couples the distress of attempting ineffective treatments.
Causes of Male Infertility
There are many possible causes of male factor infertility, including:
- Varicocele
- Low sperm count
- Low testosterone(hypogonadism)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Ejaculatory dysfunction
- Post-vasectomy fertility
- Ejaculatory duct obstruction
Testing and Evaluation of Male Fertility
There are many possible causes of male infertility and can range from environmental factors to physical issues. The main goal of testing and evaluation is to identify potentially correctible conditions, irreversible conditions and the most appropriate methods for managing those conditions. Possible testing and evaluation procedures may include:
- Review of the man's health history, including:
- Sexual history
- Pregnancy history (any previous children)
- Childhood diseases
- Medical or surgical problems
- Gonadotoxins (environmental toxins that might affect sperm development, including cigarette smoke, agricultural or other chemical agents)
- Semen analysis
- Blood hormone testing
- Sperm DNA fragmentation analysis
- Ultrasound
- Genetic testing
Treatments for Male Infertility
Treatment options vary and can include non-invasive procedures as well as more advanced treatments. Among the treatments available through our centre are
- Sperm retrieval
- Testicular Sperm Extraction/Aspiration (TESE/TESA)
- Electroejaculation (EEJ)
Treatment for Women
Fertility restoration: Stimulating ovulation with fertility drugs
Fertility drugs, which regulate or induce ovulation, are the main treatment for women who are infertile due to ovulation disorders. In general, they work like the natural hormones — follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) — to trigger ovulation.
There are several fertility drugs for abnormal LH and FSH production. These drugs include:
Clomiphene citrate . This drug is taken orally and stimulates ovulation in women who have PCOS or other ovulation disorders. It causes the pituitary gland to release more FSH and LH, which stimulate the growth of an ovarian follicle containing an egg. Clomiphene citrate also improves fertility in normally ovulating women, and is often used as an initial treatment for unexplained infertility.
Gonadotropins. Instead of stimulating the pituitary gland to release more hormones, these treatments stimulate the ovary directly. Often, gonadotropin medications are used in combination with intrauterine insemination (IUI) — a procedure during which sperm is injected into your uterus via a thin tube (catheter) — to increase the odds of a pregnancy. Gonadotropin medications include:
- Human menopausal gonadotropin, or hMG, This injected medication is for women who don't ovulate on their own due to the failure of the pituitary gland to stimulate ovulation. HMG contains both FSH and LH, and directly stimulates the ovaries to ovulate.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone, or FSH, FSH works by stimulating the ovaries to produce mature egg follicles.
- Human chorionic gonadotropin, or HCG, Used in combination with clomiphene, hMG or FSH, this drug stimulates the follicle to release its egg (ovulate).
Metformin This oral drug is used when insulin resistance is a known or suspected cause of infertility, usually in women with a diagnosis of PCOS. Metformin improves insulin resistance, normalizing the insulin level and making ovulation more likely to occur.
Fertility restoration: Surgery
Several surgical procedures can correct problems or otherwise improve female fertility. They include:
- Tubal reversal surgery (microscopic). After a woman has had her tubes tied for permanent contraception (tubal ligation), surgery may be done to reconnect them and restore fertility. Your doctor will determine whether you're a good candidate for the surgery.
- Tubal surgeries. If your fallopian tubes are blocked or filled with fluid (called hydrosalpinx), tubal surgery may improve your chances of becoming pregnant. Laparoscopic surgery is performed to remove adhesions, dilate a tube or create a new tubal opening. Tubal surgery is more successful when the blocked or narrowed part of the tube is closer to the ovary than to the uterus. Tubal blockage close to your uterus may increase your risk of ectopic pregnancy. In these and other severe cases of blockage or hydrosalpinx, removal of your tubes (salpingectomy) can improve your chances of pregnancy with in vitro fertilization.
- Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are diagnosing and treating both uterine and tubal infertility as well as some ovarian abnormalities. They have, thus, the main role in diagnosis and treatment of female infertility. They permit to correct data from the HSG in more than a quarter of cases and to improve the rate of pregnancy in more than one third of cases.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a procedure that involves placing sperm inside a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilization. This fertility treatment does not involve the manipulation of a woman’s eggs, and therefore is not considered an assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedure.
IUI
IUI is a fertility treatment that uses a catheter to place a number of washed sperm directly into the uterus. The goal of IUI is to increase the number of sperm that reach the fallopian tubes and subsequently increase the chance of fertilization.
IUI is a fertility treatment often selected by couples who have been tryingto conceive for at least one year with no success. IUI may be selected as a fertility treatment with any of the following conditions:
- Unexplained infertility
- Low sperm count
- Decreased sperm mobility
- Requirement of donor sperm
- A hostile cervical condition, such as cervical mucus that is too thick
- Cervical scar tissue from past procedures or endometriosis
- Ejaculation dysfunction
IUI provides the sperm an advantage by giving it a head start, but still requires a sperm to reach and fertilize the egg on its own.
IUI procedure is simple and may be performed even if the woman is not receiving medication to improve her egg production. Many physicians will encourage women to take medications to stimulate the ovaries to increase egg production in order to improve the chance of achieving pregnancy.
An ultrasound will be used to monitor the size of the follicles (folliclesdevelop into eggs). The hormone, human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG), is administered to stimulate the release of eggs from the follicles.
A semen sample will be washed by the lab to separate the semen from the seminal fluid. A catheter is used to inject the processed sperm directly into the uterus. This process maximizes the number of sperm cells that are placed in the uterus, thus increasing the possibility of conception. The IUI procedure takes little time and involves minimal discomfort. Women under the age of 35 usually have higher rates of success than womenover age 35, but the average success rate for IUI ranges from 10-20% inone cycle. With IUI, as with other methods of artificial insemination, thesuccess rate depends primarily on the health of both the sperm and the woman.
Reproductive assistance: In vitro fertilization
This effective technique involves retrieving mature eggs from a woman, fertilizing them with a man's sperm in a dish in a laboratory and transferring the embryos in the uterus three to five days after fertilization. In vitro fertilization (IVF) often is recommended when both fallopian tubes are blocked. It's also widely used for a number of other conditions, such as endometriosis, unexplained infertility, cervical factor infertility, male infertility and ovulation disorders. IVF increases your odds of having twins or other multiples if more than one embryo is transferred to your uterus. IVF requires frequent blood tests and routine hormone injections.
INVITRO FERTILIZATION(IVF) is commonly called as Test Tube Baby is a method of simply uniting a man’s sperm to his female partner’s egg in the lab to produce embryos. Subsequently these embryos are transferred into the uterus through the cervix after 3 to 5 days of being in the incubator for normal development. This procedure is done only when there is poor sperm quality or quantity, obstruction between the egg and sperm, ovulation problems, and sperm –egg interaction problems. Usually these problems can prevent couples from having a baby naturally and IVF helps to solve this.
TIPS BEFORE IVF TREATMENT
- Visit and discuss to your doctor about your plans to become pregnant and the difficulties you have.
- It is good time to get out your bad habits like smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Seek out support from good minded people
- Try to relax. Stress can inhibit your chance of pregnancy. Do what you find relaxing like reading books, watching TV, spending time with your family.
- Modify your diet with healthy balanced food like fruits and vegetables,2liters of water atleast/day, pre-natal supplements like folic acids.
BASIC REQUIRED TIME FOR IVF
Generally some preparation and testing is required in order to optimize IVF treatment. It is realistic to assume that you will need about 2 months to cover the topics below.
- Month 1: Tests
- Month 2: Stimulation, Egg retrieval, Embryo transfer
1. BASIC SCREENING TEST:
Before the treatment starts, you will be advised by your doctor to undergo certain tests like:
1. Lab work- This blood investigation is done on 2nd day of your cycle.
2.Partner’s Lab work: Semen analysis and few blood tests.
3.Ultrasound -Scanning for uterus and ovaries.
4.Infertility Counseling- During this period you will be explained about the treatment plan and the proposed medications, financial implications etc.
5. Any Misc- If necessary, as per the doctor order.
CONSENT TO START PROCEDURE:
Couples who have infertility have greater risks with pregnancy even if they conceive on their own without any treatment. Before the IVF treatment they will be issued with consent forms and information sheets about their treatment. We recommend that you read them carefully. Do not hesitate to ask for help from doctor or the clinic co-ordinator if there is anything you cannot fully understand. You should give your consent after you are satisfied that you understand what you are agreeing to.
1.Super ovulation:
Production of multiple eggs by high dose drug induced is known as "super ovulation". The first step in super ovulation therapy is administering the medications to women either orally or by injection to increase the levels of both LH and FSH that increases the number of mature eggs produced by the ovaries. During this process ultrasound scan is done to assess the ovarian follicles. Blood samples are also taken to measure the LH and estrogen level. Trans vaginal ultrasound examination is also done. With these reports doctor can determine the exact date of egg harvesting.
Hormonal injections (FSH or HMG) are given to stimulate the ovaries to produce more number of oocytes. The biggest advantage of these injections are they can be given subcutaneously. Symptoms such as hot flushes, headaches, abdominal distention, discomfort, restlessness, mood changes may be noticed which usually last for a short period of time which is usually released soon after the follicular aspiration.
2. HCG Injection:
The HCG injection ripens the developing eggs and initiates ovulation. If the follicular growth and the hormone levels are satisfactory, HCG injection is given usually 35-36 hours prior to the oocyte retrieval.
3. Egg Retrieval
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PRE-EGG RETRIEVAL
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight prior to the egg retrieval since you will be given general anesthesia.
- Kindly make sure to arrive without jewelry, nail polish, make up or contact lenses.
- When you are in the preparatory room, please empty your bladder.
- A mild sedative medication is given. Vaginal probe is introduced into the vagina and the eggs are retrieved with a needle inserted through the vaginal wall. You will be recovered soon from anesthesia.
- Your partner will be asked to provide a semen specimen before or immediately after the time of your retrieval.
- Two days abstinence is needed before egg retrieval for getting good quality semen sample for inseminating the oocytes.
- The patient can attend the normal work after the egg retrieval.
- The eggs are aspirated along with follicular fluid into a test tube and hand over to the laboratory for examination.
- You will be kept for observation in the recovery room for about 1- 3 hours after the retrieval.
- Following your retrieval you may eat or drink when you feel well enough.
- Sometimes when immature eggs are retrieved, your partner may be required to provide a second semen specimen the day after retrieval.
It is normal to be nervous about the procedure, but most women go through it without much trouble or pain. Anesthesiologist will give a light sedative medication intravenously to help you feel relaxed, pain free and to make you sleep during the procedure.
Once the medications take their effect, your doctor will use a transvaginal ultrasound to guide a needle through the back wall of your vagina, up to your ovaries. She will then use needle to aspirate the follicle, or gently suck the fluid and oocyte from the follicle into the test tube. There is one oocyte per follicle. These oocytes will be transferred to the embryology lab for fertilization. The number of oocytes retrieved varies but can usually be estimated before retrieval via ultrasound. The average number of oocytes is 8 to 15, with more than 95% of patients having at least one oocyte retrieved.
After the retrieval procedure, you'll be kept for a 2-3 hours to make sure all is well. Light spotting is common, as well as lower abdominal cramping, but most feel better in a day or so after the procedure.
POST-RETRIEVAL INSTRUCTIONS:
After the retrieval you may feel some pelvic area tenderness and feel tired or sleepy as you have received sedative medications during the procedure. This medication may not be eliminated by your body for upto 24 hours so you may feel just not your normal self.
- You will also have some light vaginal spotting and this bleeding should be scant and may be red to brown in color.
- As long as you are not nauseated you can eat whatever you like. Avoid spicy food for atleast 24 hours.
- Antibiotic may be administered to avoid infection following the procedure
CONTACT YOUR DOCTOR IMMIDIATELY IF ANY OF THE FOLLOWING OCCURS:
- Excessive vaginal bleeding
- High grade fever (more than100.4° F ) that last for more than 2 hours.
- Sharp and shooting paid.
- Difficulty in urination or change in bowel activity.
- Pain or burning urination.
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Unusual and increased pelvic area discomfort.
- Unusual back pain
4.EGG FERTILIZATION
When you are recovering from egg retrieval the aspirated follicles will be searched for oocytes or eggs. Once the oocytes are found, they will be evaluated. If the eggs are not matured enough, they will be stimulated for maturity in the lab. If the eggs are over mature, fertilization may not be successful.The sperms are separated from the seminal plasma and are washed to inseminate the eggs.
INTRA CYTOPLASMIC SPERM INJECTION (ICSI):
The matures eggs from the female are aspirated through the vagina using ultrasound and are incubated under precise condition in the lab. The semen sample is prepared by centrifuging so that dead sperms and other debris are separated . A single live sperm is picked up in a glass needle and injected it directly into the egg.
- No tub bath or swimming for 48 hours after the embryo transfer.
- No intercourse or orgasms until the fetal heart beat is seen on ultrasound or the pregnancy test is negative.
- No excessive physical activity such as jogging, aerobics or games.
- No heavy lifting.
- Do not take any non prescribed medications or other prescribed ones without the approval of the physician.
- Keep yourself mentally distracted from tension of anxious waiting for 14 days. Make yourself busy in reading books, listening music etc.
- Skill and experience of the team and the availability of the treatment when you want it
- Total number of embryos
- Womens follicular stimulating hormones should rise sufficiently
- Successful egg retrieval
- Pre mature ovulation should not occur
- Sperm should fertilize more than one egg
- Fertilized egg should divide and grow well for final implantation in the uterus.